Tutorial-5: Estimation of Complexity Measure V(G): For a Triangle
Objective of the Tutorial: To draw a Flow Graph, find its Cyclomatic Complexity, V(G) and the independent paths for the program reading a, b and c as the three sides of a triangle and determines whether they form an isosceles, equilateral or scalene triangle.
A brief Introduction to Basis Path Testing & measurement of Complexity Measure V(G):
Basis path testing helps a tester to compute logical complexity measure, V(G), of the code. This value of V(G), defines the maximum number of test cases to be designed by identifying basis set of execution paths to ensure that all statements are executed at least once.
Steps to compute the complexity measure, V(G) are as under
Step
1: Construct the flow graph from the source code or flow charts.
Refer Following Tutorial on :
Flow Graph and its Notations
Step 2: Identify independent paths.
Step 3: Calculate Cyclomatic Complexity, V(G).
Step 4: Design the test cases.
Starting point for the Tutorial: Is the construction of the Flow Chart followed by a Flow Graph:
Step 1: Start preparing the following Flow Chart
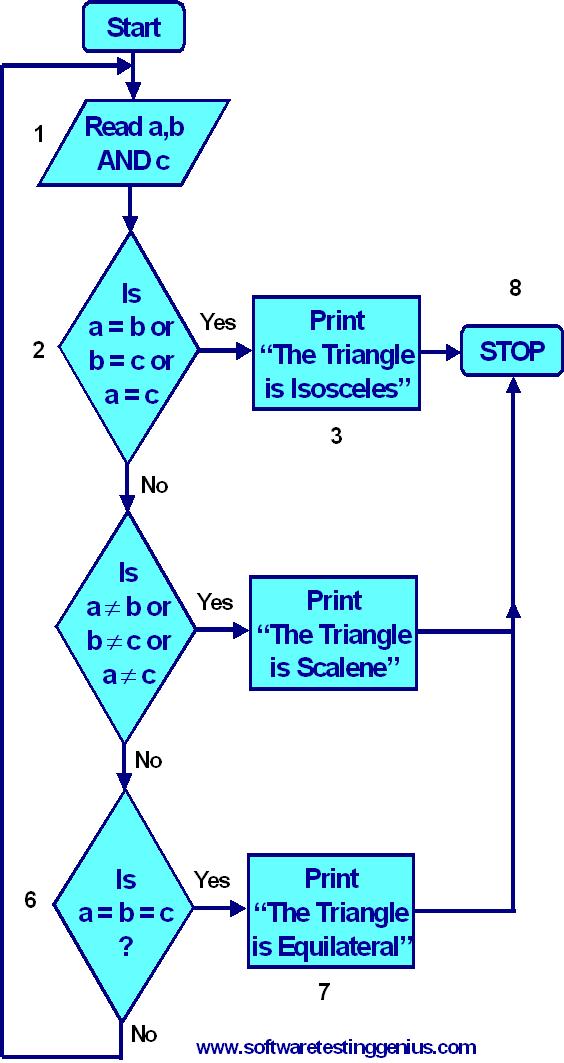
Step 2: Draw the following Flow Graph
Step 3: Calculation of Cyclomatic Complexity V(G) by three methods
Method 1: V(G) = e � n + 2 ( Where “e” are edges & “n” are nodes)
V(G) = 10� 8 + 2 = 2 + 2 = 4
Method 2: V(G) = P + 1 (Where P � No. of predicate nodes with out degree = 2)
V(G) = 3 + 1 = 4 (Nodes 2, 4 & 6 are predicate nodes with 2 outgoing edges)
Method 3: V(G) = Number of enclosed regions + 1 = 3+1=4
( Here R1, R2 & R3 are the enclosed regions and 1 corresponds to one outer region)
V(G) = 4 and is same by all the three methods.
Conclusions from the above tutorial:
The test cases for each of the path are:
Path – 1: Test case 1
a, b, c : valid input
Expected results: if s = b or b = c or a = c then message `isosceles triangle, is displayed.
Path – 2: Test case 2
a, b, c : valid input
Expected results: Expected results : if s # b * c then message `scalene triangle, is displayed.
Path – 3: Test case 3
a, b, c : valid input
Expected results: if s = b = c then message `equilateral triangle, is displayed.
Path – 4: Test case 4
a, b, c : valid float inputs and if a > 0 and b > 0 and c >0
Expected results: proper inputs-a, b and c and proper results.
Many more Articles & Tutorials on White Box Testing

An expert on R&D, Online Training and Publishing. He is M.Tech. (Honours) and is a part of the STG team since inception.
