ISTQB Agile Tester Extension Exam Theory Study Material Part 5
Have a deep study of this entire question bank containing theory portion with detailed explanation. This study resource is as per the latest syllabus.
Just 1 hr. of time spent in brushing up your knowledge just before the ISTQB Agile Tester Extension Exam shall be of great help in clearing it.
Set of 10 Questions (Q. 41 to 50) with detailed explanation
Q. 41: What are the benefits of “Retrospectives”?
1) Continuous improvement of development and testing by root cause analysis of defects.
2) Test-related improvement decisions focused on test effectiveness, test productivity, test case quality, and team satisfaction.
3) Improvement in testability of the applications, user stories, features, or system interfaces.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 42: Who participates in “Retrospectives”?
Because testing occurs in each sprint, testers play an important role in the retrospectives.
Following persons attend retrospectives.
1) Business representatives and all Scrum team members attend
the meeting.
2) It is recommended that the Product Owner should attend the meeting, but it is not essential.
3) Teams may invite any other participant as a special case.
4) The meeting is facilitated by the Scrum Master.
5) One of the team members is given the responsibility of recording the points of discussions and the items for actions in future.
All team members, testers and non-testers, can provide input on both testing and non-testing activities during retrospectives.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 43: What is Continuous Integration (CI) in agile development?
It is the practice of software development, where members of the team;
1) Merge all changes made to the software and
2) Integrate all changed components of the code at least once a day leading to multiple integrations per day for fast identification of defects.
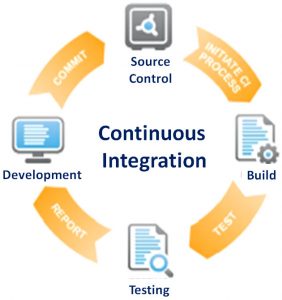
This helps in the delivery of a reliable, working, well-integrated product increment at the end of every sprint.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 44: What automated activities form a part of the continuous integration process?
1) Static code analysis: executing static code analysis and reporting results.
2) Compiling: compiling and linking the code, generating the executable files.
3) Unit testing: executing the unit tests, checking code coverage and reporting test results.
4) Deployment: installing the build into a test environment.
5) Integration testing: executing the integration tests and reporting results.
6) Reporting (dashboard): posting the status of all these activities to a publicly visible location or e-mailing status to the team.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 45: What are the benefits of Continuous Integration?
1) Early defect detection:
It permits earlier detection and easier root cause analysis of integration problems and conflicting changes.
2) Regular Feedback on quality:
It provides regular feedback to the development team on whether the code is working.
3) A shorter cycle of software version:
It helps to keep the version of the software being tested within a day of the version being developed.
4) Lower Regression Risk:
It reduces regression risk associated with developer code refactoring due to rapid re-testing of the code base after each small set of changes.
5) Improved confidence in the process:
It provides more confidence that each day’s development work is based on a solid foundation.
6) Improved visibility of process:
It Makes progress toward the completion of the product increment visible, encouraging developers and testers.
7) No big-bang integration:
It eliminates the schedule risks associated with big-bang integration.
8) Constant availability of executable software:
It provides constant availability of executable software throughout the sprint for testing, demonstration, or education purposes.
9) Less repetitive testing:
It reduces repetitive manual testing activities.
10) Quick feedback on process improvement:
It provides quick feedback on decisions made to improve quality and tests.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 46: What are the risks and challenges offered by Continuous Integration?
1) Continuous integration tools have to be introduced and maintained – tools may fail.
2) The continuous integration process adaptability – the process might not be adopted by the team.
3) Test automation requires additional resources – test automation costs are high and take a long time for establishment.
4) Thorough test coverage is essential – too much dependence on unit testing.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 47: What type of planning is done in Agile lifecycles?
Planning is an on-going activity.
For Agile lifecycles, two types of planning are done;
1) Release planning:
It is a high-level planning. It looks ahead to the release of a product, generally a few months ahead of the start of a project.
2) Iteration planning:
After the release planning is done, iteration planning for the first iteration starts.
It looks ahead to the end of a single iteration and is concerned with the iteration backlog.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 48: What is Release planning?
# It defines and re-defines the product backlog.
# It involves refining larger user stories into a collection of smaller stories.
# It provides basis for a test approach and test plan covering all iterations.
Business representatives establish and prioritize the user stories for the release, in collaboration with the team.
Based on these user stories, project and quality risks are identified and high-level effort estimation is performed.
Release plans can change as the project proceeds, including changes to individual user stories in the product backlog.
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 49: What is the role of testers in release planning?
Testers make valuable contribution in the following activities:
1) Defining testable user stories, including acceptance criteria
2) Participating in project and quality risk analyses
3) Estimating testing effort associated with the user stories
4) Defining the necessary test levels
5) Planning the testing for the release
<<<<<< =================== >>>>>>
Q. 50: What is Iteration Planning?
It involves activities like;
1) Selection of a number of user stories by the team from the prioritized release backlog – based on the team velocity and the estimated size of the selected user stories.
2) Elaboration of the user stories – means breaking down of user stories into tasks.
3) Carrying out a risk analysis for the user stories.
4) Estimation of the work needed to be done on every user story.
ISTQB Agile Tester Extension Exam Theory Study Material Part 6

An expert on R&D, Online Training and Publishing. He is M.Tech. (Honours) and is a part of the STG team since inception.
