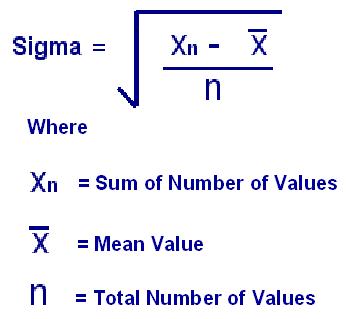
What is Six Sigma Life Cycle
Six Sigma means a measure of quality that strives for near perfection. Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects (driving towards six standard deviations between the mean and the nearest specification limit) in any process — from production to transactional and from product to service.
The statistical representation of Six Sigma describes quantitatively how a process is performing. To achieve Six Sigma, a process must not produce more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. DPMO allows us to take complexity of product / process into account. A Six Sigma defect is defined as anything outside of customer specifications. A Six Sigma opportunity is then the total quantity of chances for a defect.
The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction through the application of Six Sigma improvement projects.
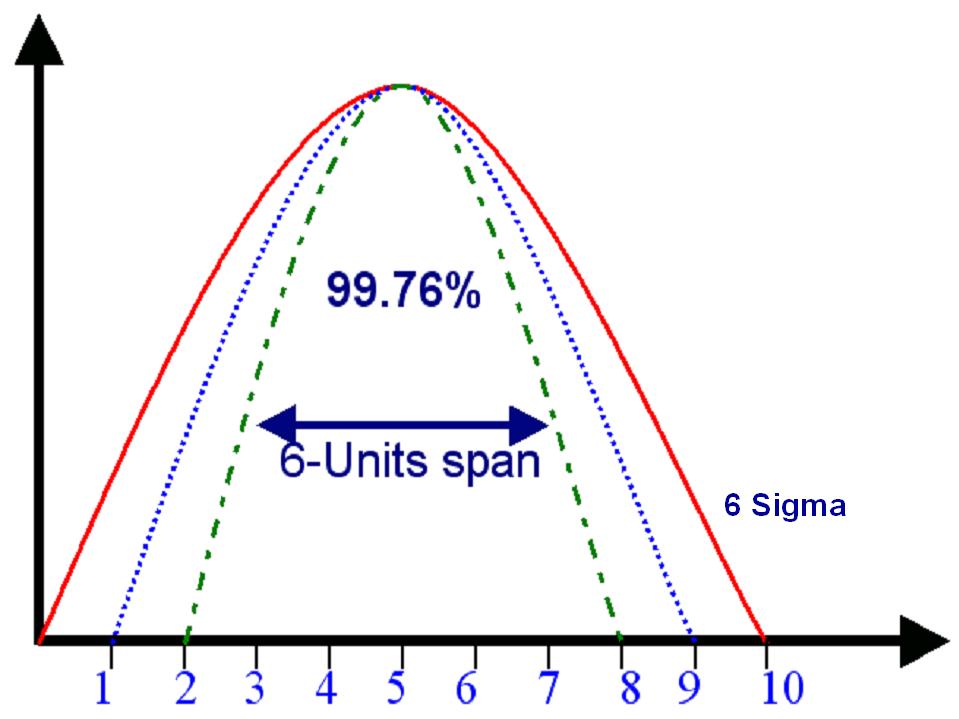
Six – Sigma companies strive to develop their product in multiple cycles; wherein for every cycle a graph is plotted. In case the plot happens to span across 6-units on the 6-sigma
axis, the product is stopped and is thoroughly checked for the Quality. This is aimed to achieve a quality level of 99.76% and more.
SSLC (Six Sigma Life Cycle): It contains following Five phases
1) Define: Here the companies define the project goals and customer (internal and external) deliverables
2) Measure: It involves measurement of the process to determine the current performance in respect to the defined values.
3) Analyze: It involves detailed analysis of the results by comparing the output values with the defined ones and finding out the root cause of the defects.
4) Improve: It involves Improvement in the process in such way to get an output with less deviation & aimed at elimination of the defects
5) Control: It involves controlling the future process performance in such a way to get the output plot / graph within 6-units span.
Broad Architecture of Six Sigma Companies:
Six Sigma is a quality methodology which can produce highly significant benefits to the companies. Although there is no hard & fast structure defined to successfully implement Six Sigma quality within a company; still some broad roles and responsibilities for a successful Six Sigma quality program are being described here.
Roles and Responsibilities:
Quality Leader (QL) / Manager (QM) – The quality leader represents the expectations of the customer and takes necessary actions to improve the operational effectiveness of the company. Generally the Quality function is separate from the production or other transaction processing functions just to exercise impartiality. The quality manager is one of the senior most executive directly reporting to the CEO of the company.
Master Black Belt (MBB) – Master Black Belts are the senior executives responsible to handle some specific important function of the company. These functions can be HR, or legal, or some other process specific areas. Master Black Belts work in tandem with the process owners & are responsible to ensure that quality objectives and targets are fixed, plans are set, progress is continuously tracked, and training is provided to the concerned. Master Black Belts closely interact with the process owners and share information on daily basis.
Process Owner (PO) – Process owners are the real doers & are responsible for specific processes. For example, in Code Development department there one head shall be there – maybe the PM / GM who becomes the process owner. According to the size of the company and major activities, there can be process owners at junior levels of the company structure.
Black Belt (BB) – Black Belts executives are the heart and soul of the Six Sigma companies. The objective of having Black Belts in the company is to provide effective leadership to the quality projects and these Black Belts work full time until the projects get completed. Black Belts are responsible to provide necessary training to their Green Belts working on their projects.
Green Belt (GB) – Green Belts are junior employees especially trained in Six Sigma. Green Belts spend a portion of their time completing various projects assigned to them in addition to their regular work role and responsibilities. Depending on their workload, they usually around10% to 50% of their time on their project(s). As the Six Sigma quality program evolves in the company, all employees start adopting the Six Sigma methodology in their daily routine & a time comes when they don�t need any percentage limit for their time. They get so much used to the new style that they start devoting 100% of their time the new way.
Many More Articles on Quality Management

An expert on R&D, Online Training and Publishing. He is M.Tech. (Honours) and is a part of the STG team since inception.