The world of Technology is now on the verge of a revolutionary change. New technologies like, artificial intelligence, robotics, digital manufacturing, autonomous vehicles, biotechnology, nanotechnology, materials science, analysis of real-time data of trillions of pieces of information, modern gadgets connected to the internet are going to evolve into a “Fourth Industrial Revolution” known as “Industry 4.0” in short.
Can India one of the biggest economic powers of the world with its 1.35 billion populate ignore the forthcoming changes? Not at all, the nation has to get ready to face the enormous challenges and be a part of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Taking one step forward, Prime Minister Mr Narendra Modi on 19th February 2018 launched eight futuristic technologies under “Digital India” initiative by the government of India.
Public, by and large, hasn’t fully realized the advent of this revolution yet, however digital technology Initiatives would bring enormous opportunities to bypass several stages of development in India. The government of India is encouraging the Indian industry and new start-ups to be a part of “The Digital Revolution” to bring India into the arc of progress sweeping the world.
New technologies launched by Prime Minister Modi are;
1) Robotic Process Automation or RPA
2) Artificial Intelligence or AI
3) Virtual Reality
4) Internet of Things (IoT)
5) Big Data Analytics
6) 3D Printing
7) Cloud Computing
8) Social and Mobile
In the “First Industrial Revolution”manufacturing sector used hydro-power and steam power to mechanize its production. In the “Second Industrial Revolution,” mass production switched to electric power. And in the “Third Industrial Revolution,”information technology became the backbone for automating the industrial production.
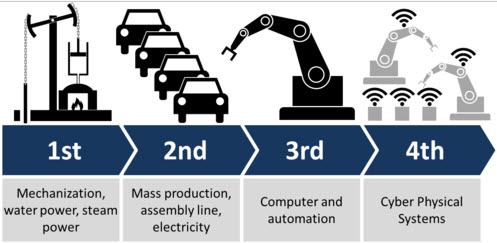
Now the “Fourth Industrial Revolution” is basically a digital revolution characterized by a fusion of many technologies and physical systems. The technology is getting deeply embedded within our society and the human bodies and this revolution are going to be unlike any other in the human history so far.
“Fourth Industrial Revolution” aims at creating “smart factories”. The smart factories to have a modular structure with cyber-physical systems in place for monitoring physical processes, creating a virtual copy of the physical world and making decentralized decisions. Over the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems communicate over the Internet of Things and cooperate with each other and with human beings in real-time.
Great progress has been made in Artificial Intelligence in recent years which can be seen in the form of surveillance drones and to virtual assistants.

Banks in India have already taken lead in deploying humanoid robots and chatbots. One can see a Kannada-speaking robotic receptionist (MITRA) guiding customers to the right counter in Canara Bank at Bengaluru. HDFC Bank has deployed Intelligent Robotic Assistant (IRA), for helping customers in selecting the right financial products and service.

IRA 2.0 Humanoid at HDFC Bank – Bangaluru

CANDI Humanoid at Canara Bank – Bangaluru
The implementation of robots in the banking sector is in a primitive stage and these humanoid are meant to perform certain basic tasks right now by offering predefined answers to the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs).
According to World Economic Forum data we can expect to see:
1) By 2025 Nanomaterials 200 times stronger than steel and a million times thinner than human hair shall be available for commercial use;
2) By 2020 the first 3D-printed liver shall be available for transplant in humans; American bio-printing company Organovo has successfully demonstrated its 3D printed liver tissue patches when implanted into mice.
3) By 2020 more than 10 million self-driving cars will be on the US road. These fully autonomous vehicles shall be able to drive from point 1 to point 2 without any interaction from the driver. Such cars are going to be smart enough to intelligently handle the entire range of on-road challenges’.
Challenges posed by “Fourth Industrial Revolution”:
1) IT security issues;
2) Reliability and stability of critical (M2M);
3) Maintaining integrity of production processes;
4) Avoiding IT snags, causing expensive production outages;
5) Protecting industrial know-how;
6) Lack of adequate skill-sets;
7) A threat of redundancy in the corporate IT department;
8) General reluctance to change by stakeholders;
9) Loss of many jobs to IT-controlled processes;
10) Low top management commitment;
11) Clarity on legal issues and data security;
12) Clarity on economic benefits/ Excessive investment;
13) Clarity on regulations, standard and forms of certifications;
14) Insufficient qualification of employees;
A Roundup:
A point of concern remains is that over-dependence on automation and robotics in industrial manufacturing would lead to job crunch in India. As such the current workforce would need relooking at skill enhancements and look for jobs in other sectors for survival. With this concern in mind, the Government of India is going to kick start Cyber-Physical Systems Mission under which Centres of Excellence are to be established for Artificial Intelligence, Robotic Process Automation, Digital manufacturing, Big Data Analysis, Internet of Things, Quantum Communications. Research, training and skill development programmes will be the focus of such centres of excellence. This may prove to be a boon for 12–13 million Indians entering the job market every year.
Many More Articles on New Technologies

An expert on R&D, Online Training and Publishing. He is M.Tech. (Honours) and is a part of the STG team since inception.

Hi, This is a very good portal for testing certifications study material. I too can help my friends with PMP certification study materials. Contact me jackthomas2k8@gmail.com
Such a Great Article!! I learned something new from your blog. Amazing stuff. I would like to follow your blog frequently. Keep Rocking!!