Evolution of G-Technology-1G to 5G
Article by: Dr. Anupriya Jain – A Guest Publisher of the article.
Wireless communication has achieved global revolution in a very short span of time and the most vibrant Indian buzzword as on date is “kar lo duniya mutthi main”. The software testing managers find great challenge in testing applications based on such dynamic technologies.
The old generation had only choice to use “wireless”, to convey an urgent message through the post offices. This wireless technology with the passage of time has undergone a tremendous change and has reached new heights of ‘4G’ technology. I am sure most of the people are not aware of the term ‘4G’. I am tempted to appraise the real meaning of ‘4G’ technology.
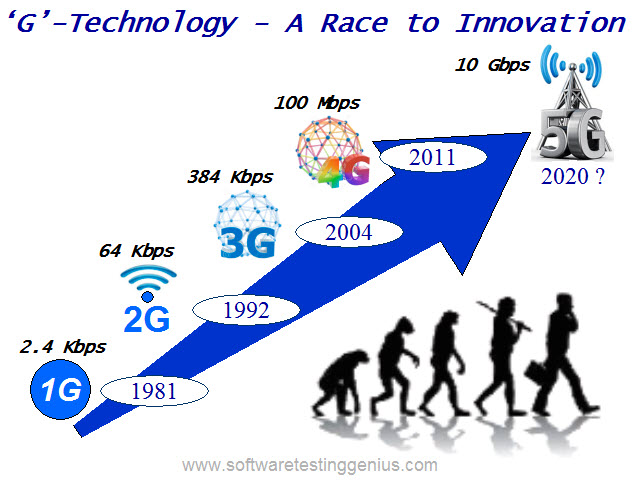
In wireless networking system the letter ‘G’ stands for Generation. Before early eighties, radio telephone system was used before the start of “Analog Cellular System” introduced by Nippon Telephone and Telegraph (NTT) Japanese corporate, which was named as ‘1G’ having data transfer rates 2.4-14.4 Kbps. The Analog Cellular systems were improper and remained operative for some time. Such cellular systems were capable for hand-over and roaming facilities only. The main drawback of these systems was that they were unable to operate across the nations.
After a decade the earlier versions of 2nd generation came into being with digital technology known as GSM (Global Systems for Mobile Communications) with data transfer rates better than 60 Kbps. It was the major jump from analog to digital technology, which supports Circuit-Switched Data (CSD) & offered improved sound quality & more security. As compared to first generation systems, the second generation used digital multiple access technology. The major limitation of this ‘2G’ technology had been the absence of cloud-based technologies, which are the backbone of the web browsing and multimedia applications as seen today.
The ‘2G’ wireless systems were voice-centric and could handle only short message service (SMS). In 2001 the third generation 3G came with fast networking technology-having data transfer rate of 384 Kbps much higher that of ‘2G’. The ‘3G’ technology has enabled web browsing, video chatting and apps downloading in a much faster and user-friendly way. This technology is being used worldwide.
‘4G’ technology is in place these days with data transfer rate of 100 Mbps and is referred as LTE (Long Term Evaluation). Cell phones, tablets and laptops, can use ‘4G’ networks. With this network technology we can avoid hurdles which were experienced in ‘3G’ models, like frequent disconnection during video chatting, buffering while watching movies on internet and ‘3G’ network.
Video chatting on cell phone or using laptops becomes much easier without any connectivity error and it gives the feeling of talking face to face irrespective of the distance. Downloading of movies, songs are now a matter of fraction of minutes. With ‘4G’ technology the problem of buffering is not seen, as all the videos get buffered in advance.
With ‘4G’ technologies it has been possible to see entire range of products by sliding screen of cell phones. This application of ‘4G’ technology popularizes the online shopping worldwide using mobile apps to access the merchant website. The worldwide popularity of Flipkart, Amazone, Jabong, Myntra, Snapdeal etc. in the field of online shopping is solely due to 4G technology.
Technology is rapidly improving and more we are likely to receive the ‘5G’ technology by 2020 having data transfer rate of 10 Gbps.
About the Author: Dr. Anupriya Jain – Assistant Professor, Ludhiana College of Engineering & Technology, Katani Kalan, Ludhiana – 141113, is a guest publisher of the article & is solely responsible for the ownership of its contents.
Contact the author: Email: npryjn111@gmail.com
Many More Articles on Software Testing Approaches

An expert on R&D, Online Training and Publishing. He is M.Tech. (Honours) and is a part of the STG team since inception.
